Java
Java
idea快捷键
ctrl+o : 查看类中所有方法
idea热部署(加依赖)
idea中springboot项目热部署最完整有效的详细配置-阿里云开发者社区 (aliyun.com)
JRebel热部署
电脑中文路径的问题暂未解决
IDEA配置JRebel热部署(超级详细图文教程)-CSDN博客
### 捡个便宜 - 交朋友吧 ### (jpy.wang)
输入 java 命令报错
java升级时,会在环境变量的path路径中增加以下两条路径,与我们安装java的路径重合。
解决方法: 删掉环境变量中的这两条语句, 同时找到对应文件,删除即可。
C:\ProgramData\Oracle\Java\javapath
C:\Program Files (x86)\Common Files\Oracle\Java\javapath
jdk
GraalVM-jdk之Windows详细安装及使用教程 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/673241258
使用IDEA 创建 SpringBoot 多模块项目_idea 建springboot module-CSDN博客
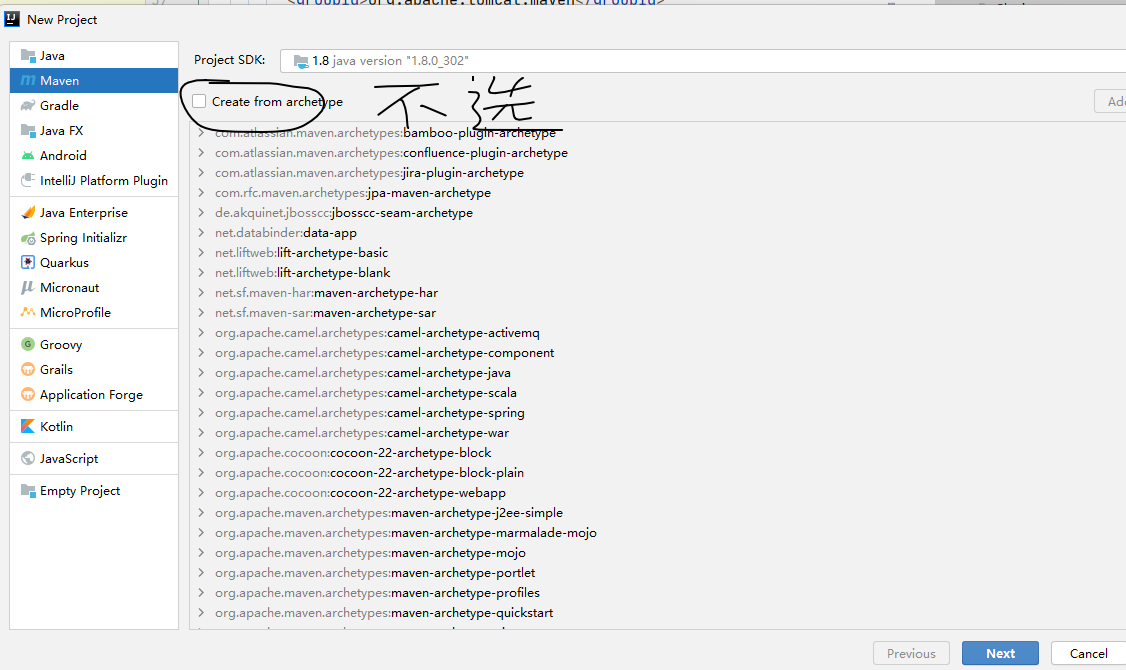
idea创建java项目(maven)
1 创建普通Java项目(quickstart)
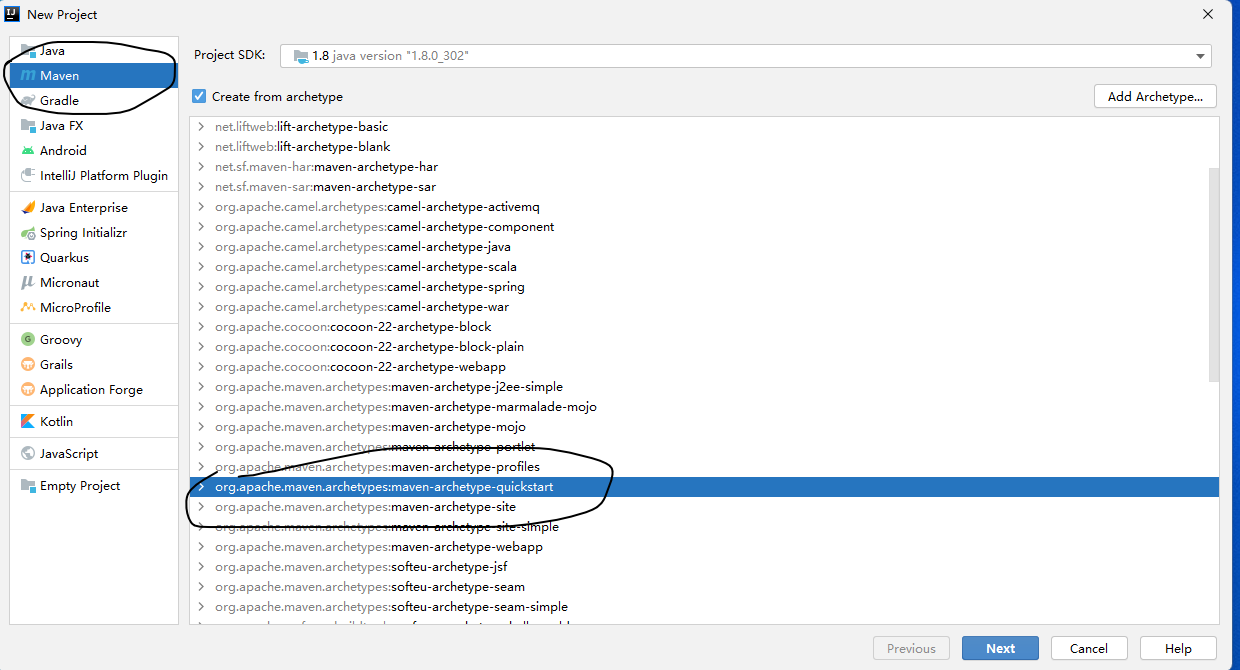
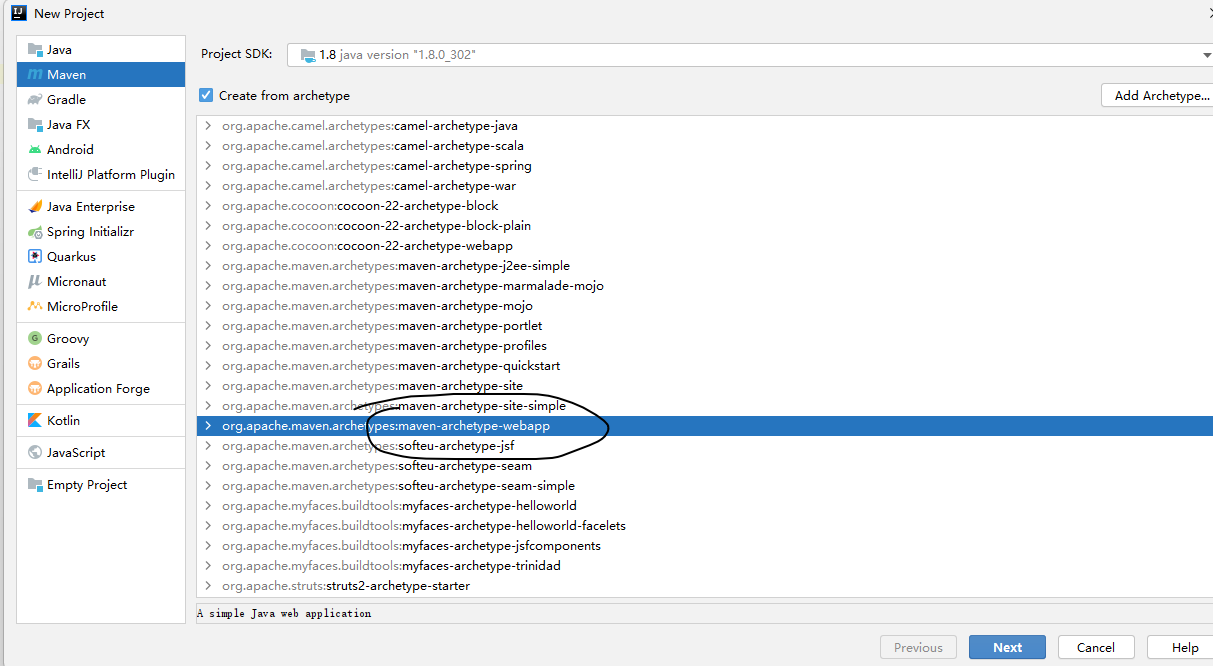
2创建普通Java web项目(maven-archetype-webapp)
pom.xml
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
删除pom.xml中 标签和里面的内容 plugins标签中加了jetty和tomcat,可以测试项目运行
<build>
<finalName>simple-java-web</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.eclipse.jetty</groupId>
<artifactId>jetty-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>9.4.11.v20180605</version>
<configuration>
<scanIntervalSeconds>10</scanIntervalSeconds>
<webAppConfig>
<contextPath>/test</contextPath>
</webAppConfig>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>8081</port> <!--启动的端口号,默认8081 -->
<path>/test</path> <!-- 项目站点名,对外访问路径 -->
<uriEncoding>UTF-8</uriEncoding>
<server>tomcat7</server>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
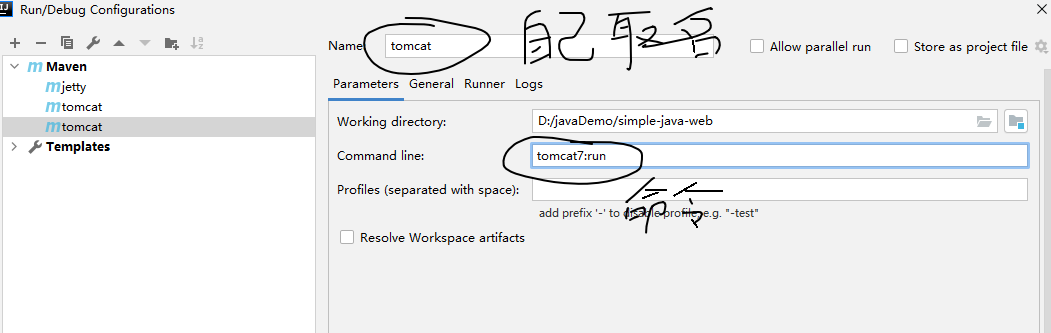
( compile命令编译 package命令打包 ) 访问路径为 : jetty http://localhost:8080/test tomcat http://localhost:8081/test
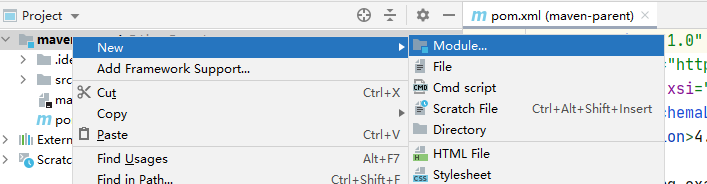
3创建多模块项目
创建项目 项目名 maven-parent
创建 module 3个
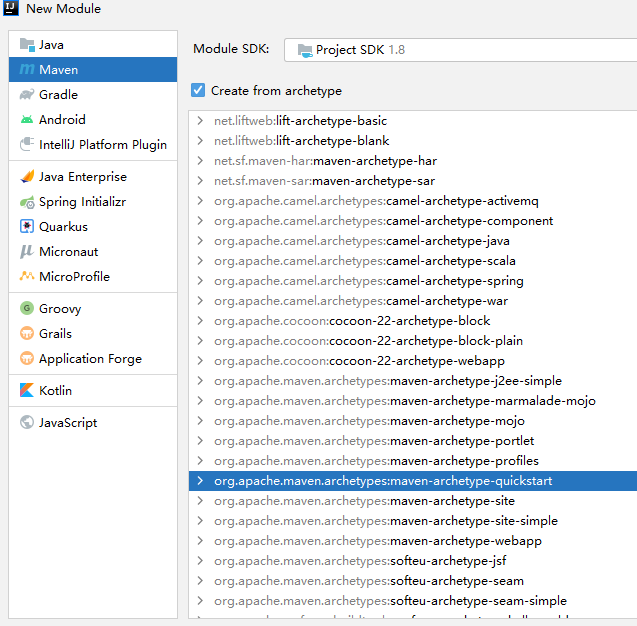
maven-dao maven-service maven-controller(3个模块) 创建maven-dao maven-service 用quickstart 创建maven-controller 用maven-archetype-webapp
生成目录结构
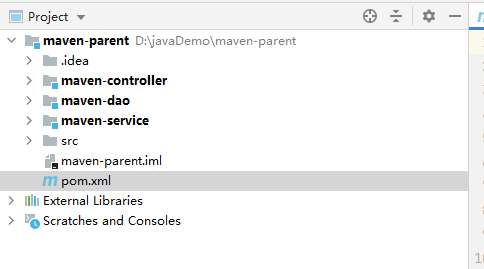
修改所有的子模块的pom.xml配置
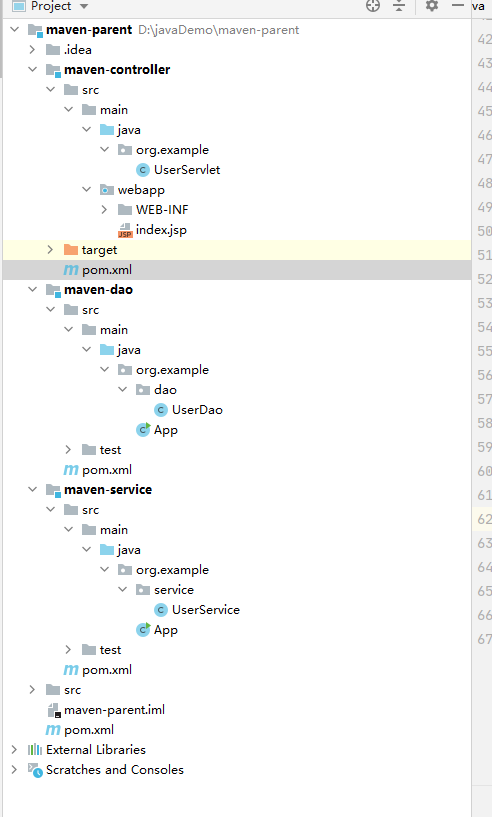
UserDao
package org.example.dao;
public class UserDao {
public static void testDao(){
System.out.println("testDao");
}
}
UserService
package org.example.service;
import org.example.dao.UserDao;
public class UserService {
public static void testService() {
System.out.println("userService");
// 调用maven-dao模块的方法
UserDao.testDao();
}
}
UserServlet
package org.example;
import org.example.service.UserService;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/user")
public class UserServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
super.service(req, resp);
System.out.println("userServlet");
UserService.testService();
}
}
在三个module的pom.xml引入相关联模块的依赖
dao不用引
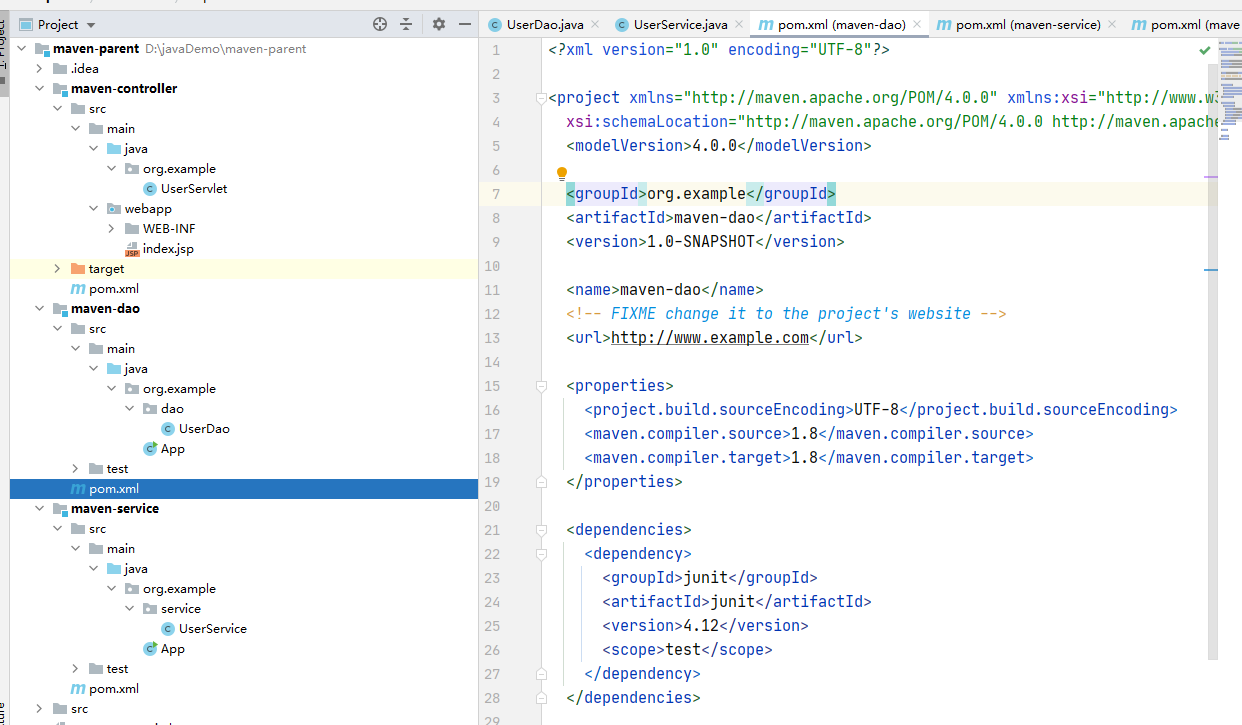
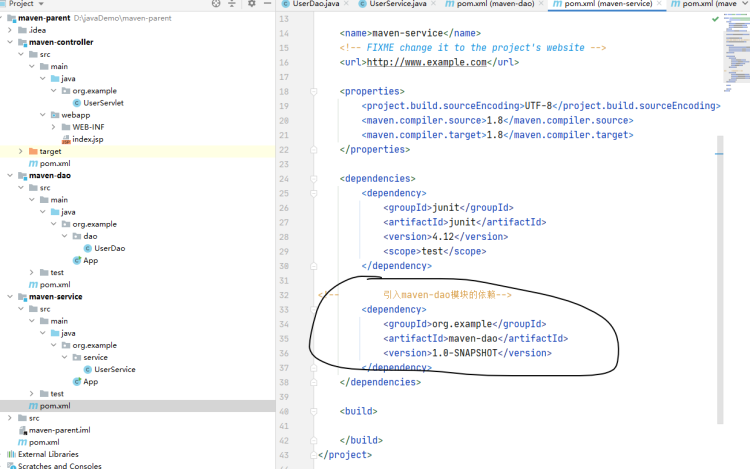
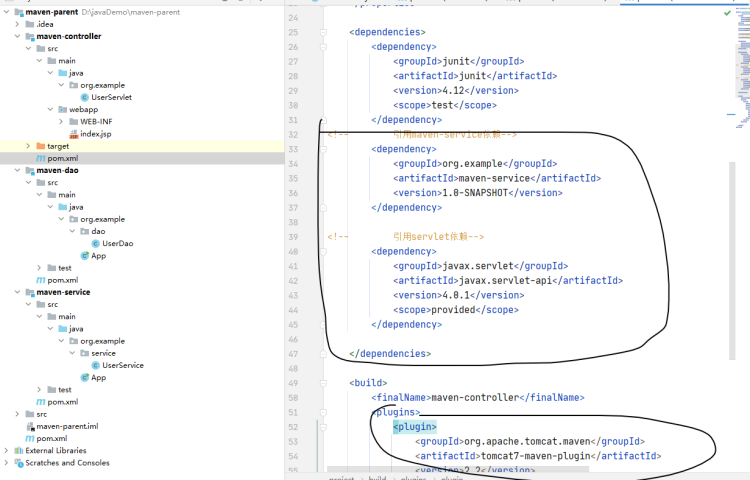
配置maven命令,启动
继承,多态
以下是简单示例:
public class Animals {
private String name;
public void move(){
System.out.println("移动");
}
public void shout(){
System.out.println("叫");
}
}
public class Dog extends Animals {
@Override
public void shout(){
System.out.println("狗叫");
}
public void dogMouse() {
System.out.println("狗吃骨头");
}
}
public class Cat extends Animals {
@Override
public void shout(){
System.out.println("猫叫");
}
public void CatMouse() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
}
@Test
void javaTest(){
// 下面展示的继承(Dog和Cat都继承Animals)
Dog dog =new Dog();
dog.move();
dog.dogMouse();
Cat cat =new Cat();
cat.move();
cat.CatMouse();
// 下面展示的多态(Dog和Cat都重写了父类的shout方法)
Animals dogs=new Dog();
dogs.shout();
Animals cats=new Cat();
cats.shout();
}
集合
https://www.runoob.com/java/java-collections.html
Collection 类关系图 | Java 全栈知识体系 (pdai.tech)
Lst系列集合:添加的元素是有序、可重复、有索引
Set系列集合:添加的元素是无序、不重复、无索引
Collection是单列集合的祖宗接口,它的功能是全部单列集合都可以继承使用的。
Java 中的集合(Collections)是一组用于存储和处理对象集合的类。Java 提供了多种集合接口和实现,主要分为两大类:List、Set 和 Map。以下是一些常用的集合操作 API 的列表,按照集合类型分类:
Collection 接口及主要实现类
https://blog.csdn.net/xing123456jl/article/details/108044431
Collection:单列集合类的根接口,用于存储一系列符合某种规则的元素,它有两个重要的子接口,分别是 java.util.List 与 java.util.Set。其中:
List 的特点是有索引、存取有序、可重复。 Set 的特点是无索引、存取无序(LinkedHashSet除外)、不可重复。
常用方法
public boolean add(E e):把给定的对象添加到当前集合中 。
public void clear():清空集合中所有的元素。
public boolean remove(E e):把给定的对象在当前集合中删除。
public boolean contains(E e):判断当前集合中是否包含给定的对象。
public boolean isEmpty():判断当前集合是否为空。
public int size():返回集合中元素的个数。
public Object[] toArray():把集合中的元素,存储到数组中。
注意:contains 细节:底层是依赖equals方法进行判断是否存在的。 所以,如果集合中存储的是自定义对象,也想通过contains方法来判断是否包含,那么在javabean类中,一定要重写equals方法。
遍历
https://blog.csdn.net/m0_51755061/article/details/115109771
迭代器遍历
Iterator迭代器接口 (1)Iterator对象称为迭代器(设计模式的一种),主要用于遍历 Collection 集合中的元素。 (2) 集合对象每次调用iterator()方法都得到一个全新的迭代器对象,默认游标都在集合的第一个元素之前。 1.1 主要方法 (1)hasNext():判断是否还有下一个元素。
(2)next():指针下移,将下移以后集合位置上的元素返回。
(3)remove():内部定义了remove(),可以在遍历的时候,删除集合中的元素。此方法不同于集合直接调用remove()
// 创建集合并添加元素
Collection<String> list = new ArrayList<String>();
list.add("1");
list.add("2");
list.add("3");
// 获取迭代器对象,迭代器就好此是个箭头,默认指向集合的0索引处
Iterator<String> iterator=list.iterator();
//利用循环不断的去获取集合中的每一个元素
while (iterator.hasNext()){
//next方法的两件事情:获取元素并移动指针
String str=iterator.next();
System.out.println(str);
}
//迭代器的细节注意点:
//1.报错NoSuchElementException
//2,迭代器遍历完毕,指针不会复位
//3.循环中只能用一次next方法
//4,迭代器通历时,不能用集合的方法进行增加或者删除,如果实在要删除:那么可以用迭代器提供的remove方法进行删除。
增强for遍历
增强 for 的底层就是迭代器,为了简化迭代器的代码书写的。 它是 JDK5 之后出现的,其内部原理就是一个 Iterator 迭代器 所有的单列集合和数组才能用增强 for 进行遍历。
// 示例:s便是list里面的每一个数据
for(String s:list){
System.out.println(s);
}
// 修改增强for 中的变量,不会改变集合中原本的数据。
Lambda表达式遍历
list.forEach(i-> System.out.println(i));
List 接口常用操作
add(E e): 向列表末尾添加一个元素。add(int index, E element): 在列表的指定位置插入一个元素。remove(int index): 删除列表中指定位置的元素。get(int index): 返回列表中指定位置的元素。set(int index, E element): 替换列表中指定位置的元素。size(): 返回列表中的元素数量。clear(): 移除列表中的所有元素。indexOf(Object o): 返回对象在列表中的第一次出现索引。lastIndexOf(Object o): 返回对象在列表中的最后一次出现索引。contains(Object o): 检查列表是否包含指定的元素。isEmpty(): 检查列表是否为空。
Set 接口常用操作
add(E e): 向集合添加一个元素。remove(Object o): 从集合中移除一个元素。contains(Object o): 检查集合是否包含指定的元素。size(): 返回集合中的元素数量。clear(): 移除集合中的所有元素。isEmpty(): 检查集合是否为空。
Set是集合体系中较为重要的接口,它具有单列存储的特点,即一次只能添加一个元素。它具有三大特点: 不可重复:当存入相同的数据时,重复的元素将会被自动去除,集合中不会有重复的值。存取顺序不一致:存入数据的顺序与输出数据的顺序不一定一致。没有带索引方法:无法使用普通for循环来遍历输出Set集合。 由于Set是一个接口,因此我们在创建Set对象时必须指定其实现类,其常用的实现类有HashSet和TreeSet。
Map 接口常用操作
put(K key, V value): 将指定的值与此映射中的指定键关联。get(Object key): 返回指定键所映射的值。remove(Object key): 从映射中移除指定键的映射关系。keySet(): 返回映射中包含的键的 Set 视图。values(): 返回映射中包含的值的 Collection 视图。entrySet(): 返回映射中包含的键值映射关系的 Set 视图。size(): 返回映射中键值映射的数量。clear(): 移除映射中的所有键值映射。isEmpty(): 检查映射是否为空。
Map接口是一个键值对的集合,它继承自Collection接口中的size()和isEmpty()等方法,同时还提供了根据键查找值的方法,以及添加、删除和更新键值对的方法。在Java中,Map接口有几个常见的实现类,每个实现类都具有不同的性能和用途。
HashMap:基于哈希表实现,具有快速的查找和插入操作,适用于需要快速查找键值对的场景。 TreeMap:基于红黑树实现,可以对键进行排序,并提供了一系列与排序相关的方法,适用于需要对键进行排序的场景。 LinkedHashMap:基于哈希表和链表实现,保持键值对的插入顺序,适用于需要保持插入顺序的场景。
Collections 类常用静态方法
sort(List<?> list): 根据元素的自然顺序对列表进行升序排序。binarySearch(List<? extends Comparable> list, Object key): 在列表中二分查找指定的对象。max(Collection<? extends T> coll): 返回给定集合中的最大元素。min(Collection<? extends T> coll): 返回给定集合中的最小元素。shuffle(List<?> list): 随机打乱列表中的元素顺序。fill(List<?> list, Object obj): 使用指定的元素填充列表。
Iterator 接口常用操作
next(): 返回迭代的下一个元素。hasNext(): 检查是否存在下一个元素。remove(): 从迭代器所连接的集合中移除当前的元素。
这些是 Java 集合框架中一些基本的操作。实际上,Java 集合框架非常丰富,包含了更多的接口和实现,以及一些高级特性,比如线程安全的集合类、队列、栈等。如果你需要更详细的信息,建议查阅 Java 官方文档或相关书籍。
java调用外部接口
SpringBoot 调用外部接口的三种方式 (qq.com)
JAVA调用第三方接口的GET/POST/PUT请求方式_java put请求-CSDN博客
Java发送Http请求(HttpClient)-阿里云开发者社区 (aliyun.com)
服务远程调用指南(RestTemplate、HttpClient)-阿里云开发者社区 (aliyun.com)
HttpClient(字符串转成对象)
依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient</artifactId>
<version>4.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpclient-cache</artifactId>
<version>4.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId>
<artifactId>httpmime</artifactId>
<version>4.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- alibaba的fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.80</version>
</dependency>
HttpClient方法封装:
package com.example.mytest.test.Util;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.apache.http.Consts;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig;
import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost;
import org.apache.http.entity.StringEntity;
import org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClients;
import org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager;
import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair;
import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import java.net.URI;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Slf4j
public class HttpClientUtil {
public static final String APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE = "application/json";
private static final Logger logger = log;
private static final Integer CONN_TIME_OUT = 3000;// 超时时间豪秒
private static final Integer SOCKET_TIME_OUT = 10000;
/** 每个路由的最大请求数,默认2 */
private static final Integer DEFAULT_MAX_PER_ROUTE = 40;
/** 最大连接数,默认20 */
private static final Integer MAX_TOTAL = 400;
private static HttpClient httpClient;
static {
// 请求配置
RequestConfig requestConfig = RequestConfig.custom()
.setConnectTimeout(CONN_TIME_OUT)
.setConnectionRequestTimeout(CONN_TIME_OUT)
.setSocketTimeout(SOCKET_TIME_OUT)
.build();
// 管理 http连接池
PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager cm = new PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager();
cm.setDefaultMaxPerRoute(DEFAULT_MAX_PER_ROUTE);
cm.setMaxTotal(MAX_TOTAL);
httpClient = HttpClients.custom()
.setConnectionManager(cm)
.setDefaultRequestConfig(requestConfig)
.build();
}
/**
* Get请求
*/
public static String requestGet(String url, Map<String, String> paramsMap) throws Exception {
//logger.info("GET request url:{} params:{}", url, paramsMap);
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<NameValuePair> params = initParams(paramsMap);
// Get请求
HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(url);
try {
// 设置参数
String str = EntityUtils.toString(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String uriStr = StringUtils.isEmpty(str) ?
httpGet.getURI().toString() : httpGet.getURI().toString() + "?" + str;
httpGet.setURI(new URI(uriStr));
// 发送请求
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpGet);
//logger.info("GET request url:{} response:{} time:{}",
// url, response, System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
// 获取返回数据
return getSuccessRetFromResp(response, url, JSON.toJSONString(paramsMap));
} finally {
// 必须释放连接,不然连接用完后会阻塞
httpGet.releaseConnection();
}
}
/**
* Post请求,Map格式数据
*/
public static String requestPost(String url, Map<String, String> paramsMap) throws Exception {
logger.info("POST request url:{} params:{}", url, paramsMap);
Long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
List<NameValuePair> params = initParams(paramsMap);
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
try {
httpPost.setEntity(new UrlEncodedFormEntity(params, Consts.UTF_8));
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
logger.info("POST request url:{} response:{} time:{}",
url, response, System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
String retStr = getSuccessRetFromResp(response, url, JSON.toJSONString(paramsMap));
return retStr;
} finally {
httpPost.releaseConnection();
}
}
/**
* Post请求,json格式数据
*
*/
public static String requestPostJsonStr(String url, String json) throws Exception {
logger.info("POST request url:{} params:{}", url, json);
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
HttpPost httpPost = new HttpPost(url);
try {
StringEntity entity = new StringEntity(json, Consts.UTF_8);
entity.setContentType(APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
httpPost.setEntity(entity);
HttpResponse response = httpClient.execute(httpPost);
logger.info("POST request url:{} response:{} time:{}",
url, response, System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
return getSuccessRetFromResp(response, url, json);
} finally {
// 资源释放
httpPost.releaseConnection();
}
}
/**
* post Object格式数据
*/
public static String requestPostJson(String url, Object obj) throws Exception {
String params = JSON.toJSONString(obj);
return requestPostJsonStr(url, params);
}
private static String getSuccessRetFromResp(HttpResponse response, String url, String params) throws Exception {
String retStr = "";
// 检验状态码,如果成功接收数据
int code = response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode();
if (code == 200) {
retStr = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), Consts.UTF_8);
} else {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("Http request error:%s, url:%s, params:%s", response, url, params));
}
//logger.info("Http request retStr:{}. url:{}", retStr, url);
return retStr;
}
private static List<NameValuePair> initParams(Map<String, String> paramsMap) {
List<NameValuePair> params = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>();
if (paramsMap == null) {
return params;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : paramsMap.entrySet()) {
params.add(new BasicNameValuePair(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()));
}
return params;
}
}
get方法获取数据测试:
@Data
public class HttpClientModel {
private String name;
private Integer age;
}
@Data
public class HttpClientModelObj {
// 变量名要和接口返回的变量名一致
private String type;
private List<HttpClientModel> data;
}
@Test
void testHttpClient() throws Exception {
// 接口返回数组
String url="http://127.0.0.1:3000/";
Map<String, String> map=new HashMap<String, String>();
String s=HttpClientUtil.requestGet(url,map );
System.out.println(s); // 接口返回数据的字符串:[{"name":"张三","age":14},{"name":"李四","age":14}]
List<HttpClientModel> list =new ArrayList<HttpClientModel>(); //创建一个变量接收数据,实体类型要和返回的数据相同
list=JSONObject.parseArray(s,HttpClientModel.class); //字符串转换成JSON格式,并转换成实体类模型,(是对象用 parseObject 方法)
list.stream().forEach(item->{
System.out.print(item.getName()); // 张三 李四
});
}
@Test
void testHttpClientObj() throws Exception {
// 接口返回对象
String url="http://127.0.0.1:3000/list";
Map<String, String> map=new HashMap<String, String>();
String s=HttpClientUtil.requestGet(url,map );
System.out.println(s); // 接口返回数据的字符串:{"type":"people","data":[{"name":"张三","age":14},{"name":"李四","age":14}]}
HttpClientModelObj httpClientModelObj=new HttpClientModelObj(); // 创建一个对象用于接收返回的数据,要求类型一致
httpClientModelObj=JSONObject.parseObject(s, HttpClientModelObj.class);
System.out.println(httpClientModelObj);
// {"type":"people","data":[{"name":"张三","age":14},{"name":"李四","age":14}]}
System.out.println(httpClientModelObj.getType());
// HttpClientModelObj(type=people, data=[HttpClientModel(name=张三, age=14), HttpClientModel(name=李四, age=14)])
System.out.println(httpClientModelObj.getData());
// [HttpClientModel(name=张三, age=14), HttpClientModel(name=李四, age=14)]
}
File
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21484461/article/details/132913531
File类
java.io.File类是Java标准库中用于表示文件和目录的类。它提供了一组方法,使您能够创建、删除、重命名、复制文件或目录,以及查询文件和目录的属性。File类的实例可以表示文件系统中的文件或目录的路径,而不必实际操作文件系统。
创建File对象
File对象既可以代表文件、也可以代表文件夹。 Fil封装的对象仅仅是一个路径名,这个路径可以是存在的,也允许是不存在的。
// 使用文件路径字符串创建(绝对路径)
String filePath="E:\\qian-study\\我的前后端分离测试项目\\my-testing-warehouse\\testFile.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
System.out.println(file.length());
// 相对路径(重点) 不带盘符,默认是直接去工程下寻找文件的(项目根目录不能有错)
String filePath2="src\\main\\resources\\file\\testFile.txt";
File file2 = new File(filePath2);
System.out.println(file2.length());
// 使用父目录和子目录创建
File parentDir = new File("E:\\qian-study\\我的前后端分离测试项目\\my-testing-warehouse");
String childFileName = "testFile.txt";
File file3 = new File(parentDir, childFileName);
- 当前工作目录:在Java中,当前工作目录通常是启动Java虚拟机时的工作目录。你可以使用
System.getProperty("user.dir")来获取当前工作目录的路径。
File对象操作方法
挺详细的:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_21484461/article/details/132913531
https://www.runoob.com/java/java-file.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/204a828531e8
java中的File类提供了许多常用的方法,用于操作文件和目录。下面是一些常用的File类方法:
文件和目录的创建、删除和重命名:createNewFile()、delete()、renameTo(File dest)。
检查文件或目录是否存在:exists()。
获取文件或目录的属性:如length()(大小)、lastModified()(最后修改时间)。
列出目录内容:list()、listFiles()。
检查是文件还是目录:isFile()、isDirectory()。
创建和删除目录:mkdir()、mkdirs()。
遍历目录,列出目录下的文件和子目录
只列出直接的子文件和子目录
要列出目录下的文件和子目录,可以使用list()方法和listFiles()方法。list()方法返回一个字符串数组,包含目录下的所有文件和子目录的名称。listFiles()方法返回一个File数组,包含目录下的所有文件和子目录的File对象。
// 只列出直接的子文件和子目录
File dir=new File("src\\main\\resources\\file");
String[] children = dir.list();
if (children != null) {
for (String child : children) {
System.out.println(child);
}
}
File[] childFiles = dir.listFiles();
if (childFiles != null) {
for (File childFile : childFiles) {
System.out.println(childFile.getName());
}
}
递归遍历子目录
如果目录下还有子目录,您可能需要递归地遍历整个目录树。
File dir=new File("src\\main\\resources\\file");
// 调用方法开始遍历
listFilesAndDirs(dir);
public static void listFilesAndDirs(File dir) {
File[] childFiles = dir.listFiles();
if (childFiles != null) {
for (File childFile : childFiles) {
if (childFile.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("目录:" + childFile.getName());
listFilesAndDirs(childFile); // 递归遍历子目录
} else {
System.out.println("文件:" + childFile.getName());
}
}
}
}
IO流
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44715943/article/details/116501936
什么是IO流
- I : Input
- O : Output
通过IO可以完成硬盘文件的读和写。
流的分类:
输入流、输出流字节流、字符流字节流
- 字符流
注意:
四大家族的首领都是抽象类。(abstract class) 所有的流都实现了: java.io.Closeable接口,都是可关闭的,都有 close() 方法。 流是一个管道,这个是内存和硬盘之间的通道,用完之后一定要关闭,不然会耗费(占用)很多资源。养成好习惯,用完流一定要关闭。
所有的 输出流 都实现了: java.io.Flushable接口,都是可刷新的,都有 flush() 方法。 养成一个好习惯,输出流在最终输出之后,一定要记得flush()刷新一下。这个刷新表示将通道/管道当中剩余未输出的数据强行输出完(清空管道!)刷新的作用就是清空管道。
ps:如果没有flush()可能会导致丢失数据。
在java中只要“类名”以 Stream 结尾的都是字节流。以“ Reader/Writer ”结尾的都是字符流。
java SSM框架
决定看ssm框架视频, 【尚硅谷】SSM框架全套教程,MyBatis+Spring+SpringMVC+SSM整合一套通关_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 。
需要资料当然要到评论区取找了,资源链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1jx1hRb7ugMFFJP81Fvcy1Q?pwd=yyds 提取码:yyds 。 https://gitee.com/zhengguangqq/ssm-md 尚硅谷的ssm md格式笔记
尚硅谷SSM新版视频教程-2023版 B站直达:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1AP411s7D7 百度网盘:https://pan.baidu.com/s/12roPcN1oBmDKk3wwnMSu_A?pwd=yyds 提取码:yyds 阿里云盘:https://www.aliyundrive.com/s/SGmyMwGpsZv(教程配套资料请从百度网盘下载)
资料 : 教案 · 东方凝洛/尚硅谷ssm-springboot-2023视频资料 - 码云 - 开源中国 (gitee.com)
myBatis
官网:mybatis – MyBatis 3 | 简介 MyBatis中文网
MyBatis 动态 SQL 最全教程,这样写 SQL 太爽了! (qq.com)
MyBatis-plus
官网: 简介 | MyBatis-Plus (baomidou.com)
MyBatis-plus最详细的入门使用教程来了 (qq.com)
黑马视频:day01-MybatisPlus - 飞书云文档 (feishu.cn)
MybatisPlus - 2小时入门 (ydlclass.com)
mybatis-flex
官网:https://mybatis-flex.com/zh/intro/what-is-mybatisflex.html
仓库:https://gitee.com/mybatis-flex/mybatis-flex#english--简体中文
视频教程: https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV11h411A7cU/?spm_id_from=333.788
和其他mybatis框架的区别:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/669378593
基础使用:https://juejin.cn/post/7306192146768183311#heading-7
mysql
视频学习: 01-MySQL教程简介_哔哩哔哩_bilibili 资料: /mysql/尚硅谷视频老师笔记
【狂神-MySQL】MySQL全部详细知识点整理(共10章)狂神 mysql-Blue.的博客-CSDN博客
查询结构:
#方式1:
SELECT ...,....,...
FROM ...,...,....
WHERE 多表的连接条件
AND 不包含组函数的过滤条件
GROUP BY ...,...
HAVING 包含组函数的过滤条件
ORDER BY ... ASC/DESC
LIMIT ...,...
#方式2:
SELECT ...,....,...
FROM ... JOIN ...
ON 多表的连接条件
JOIN ...
ON ...
WHERE 不包含组函数的过滤条件
AND/OR 不包含组函数的过滤条件
GROUP BY ...,...
HAVING 包含组函数的过滤条件
ORDER BY ... ASC/DESC
LIMIT ...,...
#其中:
#(1)from:从哪些表中筛选
#(2)on:关联多表查询时,去除笛卡尔积
#(3)where:从表中筛选的条件
#(4)group by:分组依据
#(5)having:在统计结果中再次筛选
#(6)order by:排序
#(7)limit:分页
SELECT 查询时的执行顺序
你需要记住 SELECT 查询时的两个顺序:
1. 关键字的顺序是不能颠倒的:
SELECT ... FROM ... WHERE ... GROUP BY ... HAVING ... ORDER BY ... LIMIT...
2.SELECT 语句的执行顺序(在 MySQL 和 Oracle 中,SELECT 执行顺序基本相同):
FROM -> WHERE -> GROUP BY -> HAVING -> SELECT 的字段 -> DISTINCT -> ORDER BY -> LIMIT
MySQL建表时注意什么?
MVSQL建表的经验有很多,下边列举一些:
- 1、注意选择存储引擎,如果要支持事务需要选择InnoDB。
- 2、注意字段类型的选择,对于日期类型如果要记录时分秒建议使用datetime,只记录年月日使用date类型,对于 字符类型的选择,固定长度字段选择char,不固定长度的字段选择varchar,varchar比char节省空间但速度没有 char快;对于内容介绍类的长广文本字段使用text或longtext类型:如果存储图片等二进制数据使用blob或 longblob类型;对金额字段建议使用DECIMAL;对于数值类型的字段在确保取值范围足够的前提下尽量使用占用 空间较小的类型
- 3、主键字段建议使用自然主键,不要有业务意义,建议使用int unsigned类型,特殊场景使用bigint类型。
- 4、如果要存储text、blob字段建议单独建一张表,使用外键关联。
- 5、尽量不要定义外键,保证表的独立性,可以存在外键意义的字段。
- 6、设置字段默认值,比如:状态、创建时间等。
- 7、每个字段写清楚注释。
- 8、注意字段的约束,比如:非空、唯一、主键等
- 时间类型选择:https://blog.csdn.net/m0_48805880/article/details/126423801 (推荐优先使用 datetime )
表关系(一对多、多对多...)
MySQL表设计思路(一对多、多对多...)_mysql一对多表设计-CSDN博客
参考:Kimi.ai - 帮你看更大的世界 (moonshot.cn)
数据库设计参考
学生成绩管理系统数据库设计--MySQL_学生成绩管理数据库-CSDN博客
点餐系统数据库设计--SQL Server_数据库学生信息管理系统项目立项书-CSDN博客
